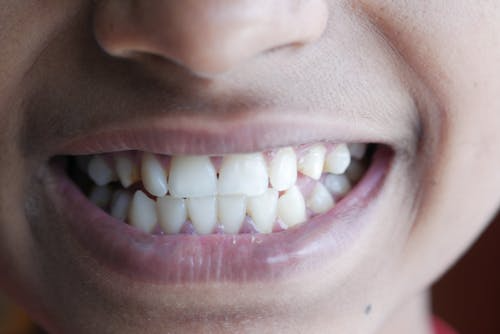
Gums play a major role in protecting your teeth and anchoring them in place. When gums start to pull away, they expose sensitive roots, which can cause discomfort and increase the risk of decay or even tooth loss.
If you’ve noticed your teeth looking longer or have felt increased sensitivity, you might be facing gum recession. The good news? Receding gums are treatable—and the sooner you act, the better the outcome.
In this Council Oak Perio guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about receding gum treatment, from causes and symptoms to professional solutions and expert care options.
Receding gums, or gingival recession, happen when the gum tissue surrounding your teeth wears away or pulls back. This leaves more of your tooth—or even the root—exposed.
It’s a common problem that affects people of all ages, not just the elderly. Once the gums recede, they don’t grow back naturally, making early treatment essential.
At first, you may not notice anything at all. But as recession progresses, your teeth may start to feel more sensitive, look longer, or develop notches near the gumline.
Over time, without treatment, the recession can lead to serious damage to the supporting bone structure and even tooth loss.
Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease that causes redness, swelling, and bleeding. Receding gums, on the other hand, are a result of gum tissue loss.
Gingivitis can lead to gum recession if left untreated, but the two are not the same. It’s important to catch gingivitis early to avoid future gum recession.
Understanding what causes your gums to recede helps you make better choices for prevention and treatment.
Brushing too hard or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can wear away at your gum tissue. It’s like using sandpaper on silk—effective at first, but damaging over time.
This is the most common cause of gum recession. It’s a bacterial infection that affects your gums and bone. If untreated, it breaks down the supporting tissues and structures of your teeth.
When plaque builds up along the gumline and isn’t removed regularly, it turns into tartar, leading to gum irritation and eventually, gum recession. Consistent brushing and flossing are key.
Changes in hormones during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can make gums more sensitive. As we age, gums naturally tend to recede, especially if oral care hasn’t been ideal.
Some people are more prone to gum disease and recession due to their genetics. If your parents had gum issues, it’s smart to be proactive about your own gum health.
Recognizing the signs early can make a big difference in the treatment outcome.
Feeling discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods? That could be a sign that your gums are pulling away and exposing the tooth roots.
If your teeth appear longer than they used to, it’s not an illusion. Gum recession makes the tooth more visible and gives this “long-tooth” effect.
Do your gums bleed when you brush or floss? This may signal the beginning of gum issues, including recession. Don’t ignore it.
Take a close look in the mirror. If you see notches at the base of your teeth or uneven gumlines, gum recession may be starting.
Getting a professional diagnosis is crucial for creating the right treatment plan.
During your dental visit, the dentist or periodontist will visually inspect your gums, measure pocket depths, and possibly take X-rays to check bone levels.
This involves using a tiny probe to measure the gap between your teeth and gums. Healthy gums measure between 1–3 mm. Anything deeper could indicate gum disease or recession.
| Pocket Depth (mm) | What It Means |
| 1–3 | Healthy gums |
| 4–5 | Mild gum recession |
| 6–7 | Moderate gum recession |
| 8+ | Severe gum recession |
X-rays help identify bone loss and how deep the problem goes beneath the surface, offering a full picture for better treatment planning.
For mild cases, non-surgical options may be enough to slow or stop gum recession.
This deep-cleaning method removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline. It smooths the root surfaces, allowing gums to reattach more easily.
Medicated rinses and antibiotics can help control bacterial infections and inflammation, giving your gums a chance to heal.
Fluoride helps strengthen enamel and reduce discomfort caused by exposed tooth roots. It’s commonly used after deep cleaning procedures.
If you grind your teeth at night, it puts pressure on your gums. A night guard protects your teeth and minimizes damage to your gum tissue.
For more advanced cases, surgical intervention may be required to restore gum health and appearance.
Gum grafting involves taking tissue from one area and attaching it where the gum has receded. This not only protects the tooth root but also improves your smile.
Tissue is taken from beneath the surface of your palate and attached to the affected area. This is the most common graft used for root coverage.
A thin layer of tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth and applied to the receding area. This method is especially helpful when the gums are thin.
This modern technique involves creating a small hole and gently shifting the gum tissue into place—no scalpels, no stitches, and faster healing.
If bone loss has occurred, regenerative techniques like membranes, bone grafts, and proteins can help rebuild the bone and support the gum tissue.
Making small changes at home can make a big difference in maintaining gum health.
Choose soft bristles that clean gently without irritating your gums. It’s an easy switch with lasting benefits.
Brush with circular motions and be gentle. Floss carefully without snapping it between your teeth. Technique matters just as much as consistency.
Smoking and heavy drinking dry out the mouth and slow healing. Reducing or quitting can dramatically improve your gum health.
Eat foods rich in Vitamin C, calcium, and healthy fats. Avoid sugary snacks and acidic drinks that can harm enamel and gums.
Ongoing care helps prevent further gum damage and catches early signs of issues.
Regular dental visits at Council Oak Perio keep plaque in check and allow your dentist to monitor any changes in your gum health.
Keeping track of pocket depth helps determine whether treatments are working or if further intervention is needed.
Pay attention to symptoms like bleeding, swelling, or sensitivity. These can indicate that recession is returning and needs to be addressed quickly.
Are you avoiding certain foods because chewing has become painful? Do you feel embarrassed by a "gummy" smile or worry about gum disease and bone loss? Council Oak Perio understands these struggles and offers expert solutions tailored to your needs.
Led by Dr. Christopher Bingham, a board-certified periodontist with over 20 years of experience, Council Oak Perio provides expert care for all stages of gum recession.
Whether you need a consultation, gum grafting, or full periodontal care, you’ll receive treatment that’s precise, personalized, and compassionate.
Our office located at 2152 Village Park Avenue, Suite 100, Twin Falls, Idaho 83301 is open Monday through Thursday from 7:30 a.m. to 3:30 p.m. and is closed on Fridays, Saturdays, and Sundays.
Ready to take the first step toward a healthier smile? Schedule your consultation with Council Oak Perio today and discover why patients trust us with their gum health.
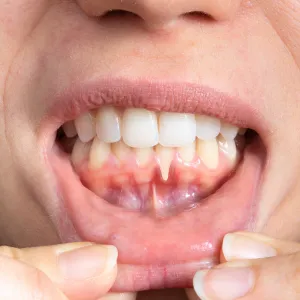
Receding gums don’t just affect how your smile looks—they impact your overall oral health.
Fortunately, with early detection, good habits, and professional care, you can manage and even reverse the effects. Whether you choose non-surgical approaches or more advanced procedures like grafting, there’s a path to recovery.
And remember, expert providers like Council Oak Perio are here to guide you every step of the way. Don’t wait until discomfort becomes damage. Take control of your gum health today.
No, once gum tissue is lost, it doesn’t grow back on its own. However, treatment can stop the progression and even restore the gumline with grafting procedures.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and most patients report only mild discomfort afterward. Over-the-counter medications usually handle the soreness.
Recovery usually takes about one to two weeks. Most people can return to normal activities within a few days, but you’ll need to follow post-op instructions carefully.
Laser therapy can be effective for treating gum disease but doesn’t replace tissue that’s already receded. It's often used alongside other treatments.
Yes, with good oral hygiene, regular dental visits, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking, you can prevent gum recession or catch it early.
A soft-bristled or electric toothbrush with a pressure sensor is ideal. It cleans effectively while protecting delicate gum tissue.